Exchange 2010 Site Resilient DAGs and Majority Node Set Clustering – Part 3
Welcome to Part 3 of Exchange 2010 Site Resilient DAGs and Majority Node Set Clustering. In Part 1, I discussed what Majority Node Set Clustering is and how it works with Exchange Site Resilience when you have one DAG member in a Primary Site and one DAG member in a Failover Site. In Part 2, I discussed how Majority Node Set Clustering works with Exchange Site Resileince when you have two DAG members in a Primary Site and one DAG member in a Failover Site. In this Part, I will show an example of how Majority Node Set Clustering works with Exchange Site Resilience when you have two DAG members in a Primary Site and two DAG members in a Failover Site.
Part 3
Real World Examples
Each of these examples will show DAG Models with a Primary Site and a Failover Site.
4 Node DAG (Two in Primary and Two in Failover)
In the following screenshot, we have 4 Servers. Four are Exchange 2010 Multi-Role Servers; two in the Primary Site and two in the Failover Site. The Cluster Service is running only on the four Exchange Multi-Role Servers. More specifically, it would run on the Exchange 2010 Servers that have the Mailbox Server Role. When Exchange 2010 utilizes an even number of Nodes, it utilizes Node Majority with File Share Witness. If you have dedicated HUB and/or HUB/CAS Servers, you can place the File Share Witness on those Servers. However, the File Share Witness cannot be placed on the Mailbox Server Role.
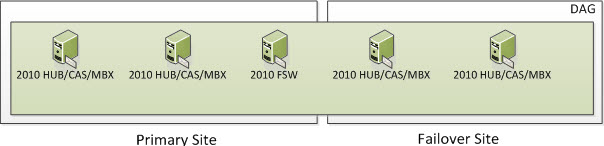
So now we have our five Servers; four of them being Exchange. This means we have five voters. Four of the Mailbox Servers that are running the cluster service are voters and the File Share Witness is a witness that the voters use to maintain cluster quorum. So the question is, how many voters/servers/cluster objects can I lose? Well if you read the section on Majority Node Set (which you have to understand), you know the formula is (number of nodes /2) + 1. This means we have (4 Exchange Servers / 2) = 2 + 1 = 3. This means that 3 cluster objects must always be online for your Exchange Cluster to remain operational.
But now let’s say one or two of your Exchange Servers go offline. Well, you still have at least three cluster objects online. This means your cluster will be still be operational. If all users/services were utilizing the Primary Site, then everything continues to remain completely operational. If you were sending SMTP to the one of the servers in the Failover Site or users were for some reason connecting to the Failover Site, they will need to be pointed to another Exchange Server that is operational in the Primary Site or the Failover Site. This of course depends on whether the user databases are being replicated from a mailbox database failover standpoint.
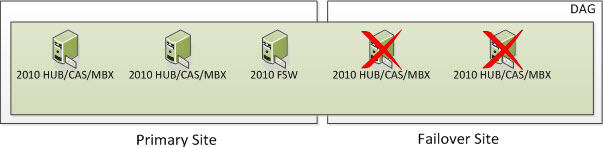
But what happens if you lose a third node in which all DAG members in the Failover Site go offline including the FSW? Well, based on the formula above we need to ensure we have 3 cluster objects operational at all times. At this time, the entire cluster goes offline. You need to go through steps provided in the site switchover process but in this case, you would be activating the Primary Site and specify a new Alternative File Share Witness Server that exists in the Primary Site so you can active the Exchange 2010 Server in the Primary Site. The DAG will actively use the File Share Witness since there will be 2 Exchange DAG Members remaining which is an even number of nodes. And again, when you have an even number of nodes, you will use a File Share Witness.
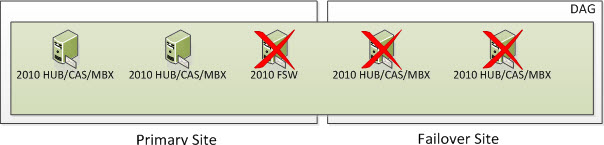
But what happens if you lose two nodes in the Primary Site as well as the FSW due to something such as Power Failure or a Natural Disaster? Well, based on the formula above we need to ensure we have 3 cluster objects operational at all times. At this time, the entire cluster goes offline. You need to go through steps provided in the site switchover process but in this case, you would be activating the Failover Site and specify a new Alternative File Share Witness Server that exists (or will exist) in the Failover Site so you can activate the Exchange 2010 Servers in the Failover Site. The DAG will actively use the Alternate File Share Witness since there will be 2 Exchange DAG Members remaining which is an even number of nodes. And again, when you have an even number of nodes, you will use a File Share Witness.
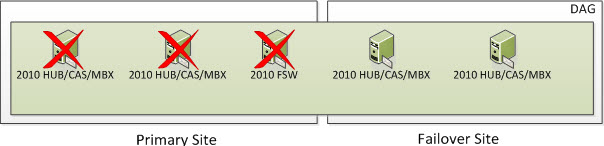
Once the Datacenter Switchover has occurred, you will be in a state that looks as such. An Alternate File Share Witness is not for redundancy for your 2010 FSW that was in your Primary Site. It’s used only during a Datacenter Switchover which is a manual process.
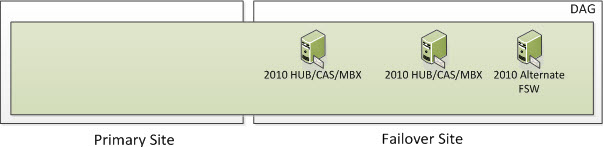
Once your Primary Site becomes operational, you will re-add the two Primary DAG Servers to the existing DAG which will still be using the 2010 Alternate FSW Server in the Failover Site and you will now be switched into a Node Majority with File Share Witness Cluster instead of just Node Majority. Remember I said with an odd number of DAG Servers, you will be in Majority Node Witness and with an even number, the Cluster will automatically switch itself to Node Majority with File Share Witness? You will now be in a state that looks as such.
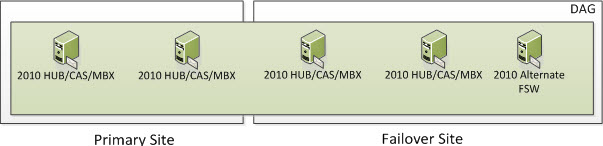
Part of the Failback Process would be to switch back to the old FSW Server in the Primary Site. Once done, you will be back into your original operational state.

As you can see with how this works, the question that may arise is where to put your FSW? Well, it should be in the Primary Site with the most users or the site that has the most important users. With that in mind, I bet another question arises? Well, why with the most users or the most important users? Because some environments may want to use the above with an Active/Active Model instead of an Active/Passive. Some databases may be activated in both sites. But, with that, if the WAN link goes down, the Exchange 2010 Server in the Failover Site loses quorum since it can’t contact at least 2 other cluster objects. Again, you must have three cluster objects online. This also means that each cluster object must be able to see two other cluster objects. Because of that, the Exchange 2010 Server will go completely offline.
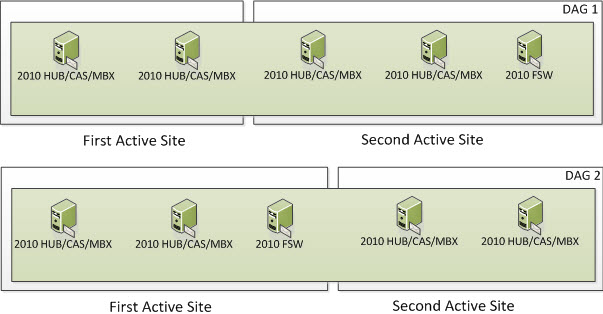
To survive this, you really must use 2 different DAGs. One DAG where the FSW is in the First Site and a second DAG where its FSW is in the Second Site. In my example, users that live in the First Active Site would primarily be using the Exchange 2010 DAG Members in the First Active Site which would be on DAG 2. Users that live in the Second Active Site would primarily be using the Exchange 2010 DAG Members in the Second Active Site which would be on DAG 1. This way, if anything happens with the WAN link, users in the First Active Site would still be operational as the FSW for their DAG is in the First Active Site and DAG 2 would maintain Quorum. Users in the Second Active Site would still be operational as the FSW for their DAG is in the Second Active Site and DAG 1 would maintain Quorum.
Note: This would require twice the amount of servers since a DAG Member cannot be a part of more than one DAG. As shown below, each visual representation below of a 2010 HUB/CAS/MBX is a separate server.
The Multi-DAG Model would look like this.
Categorised as: Exchange, Microsoft
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.